Depending on whether a condition is true or false, the IF function returns various values. In the form =IF, use it (Condition, True, False). For instance, the expression =IF(C2>=60,”Pass”,”Fail”) returns “Pass” if the value in C2 is greater than or equal to 60 and “Fail” otherwise.
Start by launching your spreadsheet with Microsoft Excel. Then, click the cell in which you want to use the function. In the following example, we’ll use the IF function to say Pass if the obtained score is 60 or higher and fail if the score is 59 or lower. We’ll select the D4 cell where we want to display the result.
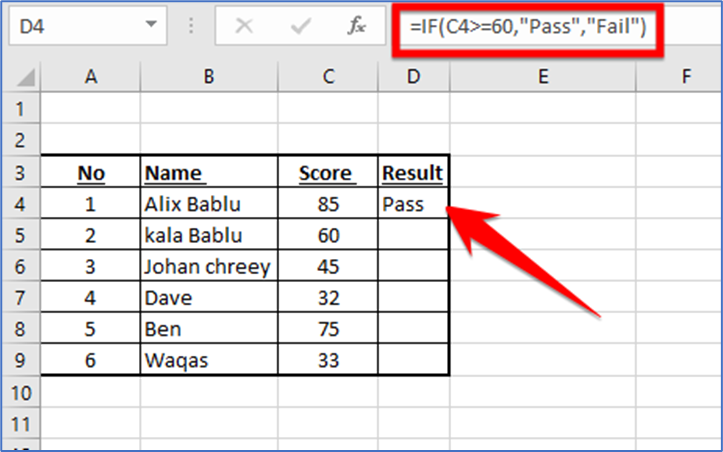
In the D4 cell, we’ll enter the following function and press Enter.
=IF(C4>=60,”Pass”,”Fail”)
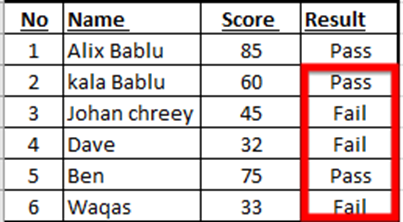
To copy the function for all your records, from the bottom-right corner of the D4 cell, drag downwards to cover all your records.
Utilize Excel’s Nested IF Function.
An IF function nested inside another IF function is known as a nested IF. When you want to conduct a second logical test after the first one, you use this. The following dataset will be used to illustrate this function
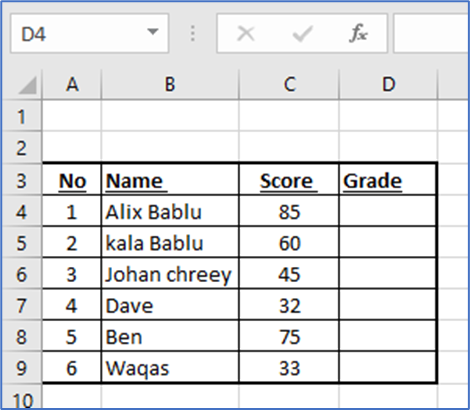
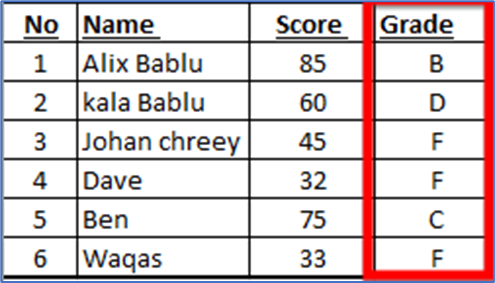
· If the score is 90 or higher: A
· If the score is between 80 and 89: B
· If the score is between 70 and 79: C
· If the score is between 60 and 69: D
· If the score is between 0 and 59: F
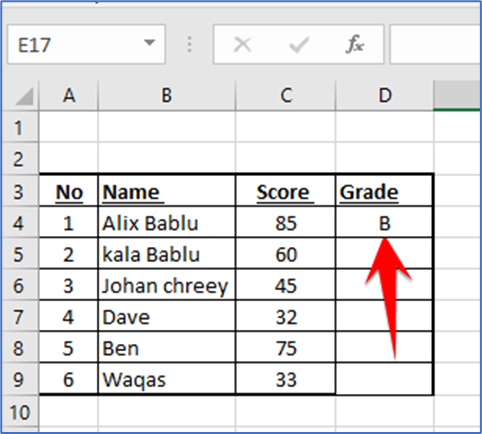
We’ll select the D2 cell where we want to display the result, and then enter the following nested IF function and press Enter:
=IF(C4>=90,”A”,IF(C4>=80,”B”,IF(C4>=70,”C”,IF(C4>=60,”D”,IF(C4>=0,”F”)))))
The IF function in Excel is a great tool for performing various logical tests. It allows you to specify a variety of criteria and display the outcomes appropriately.